Bilateral graphs are commonly used in economics because of how easy you can compare multiple variables. A bilateral graph shows multiple bar graphs grouped together by a common variable. the One above groups three seperate variables by another variable which is the year. Export, mport, and total Trade are the bilateral bars that are grouped together by year.
Monday, April 2, 2012
Unstandardized Choropleth Map
http://www.censusscope.org/us/map_common_race.html
Unstandardized Choropleth Maps are used to show a variable across a geographical area. What differs an unstandardized choropleth map from other choropleth map is that it shows the data in a uniform setting, and put to a percent. Not all maps are put to a standard scale, the above unstandardized map is comparing different ethnicities across the US.
DRG
http://infoecho.net/cschin/topo3d/
DRG or Digital Raster Graphic is a topograhpic map that is scanned and used to show features of a map. They are used in mpa making because of how in detail it can show the physical features of an area. The above picture is of Yosemite National Park. Raster Graphics are created by the USGS and are printed with a resolution of 250 dots per inch.
Cartographic Animations
Cartographic Animations are used to show maps as an animation, much like a moving picture in geography. Cartographic Animations are very useful in showing the movement of an object over a landmass, like the above example of a hurricane nearing the United States. Or cartographic animations could be used to show a flood plain, and how it is effected by rising river levels.
Planimetric Map
http://proceedings.esri.com/library/userconf/proc01/professional/papers/pap949/p949.htm
Planimetric maps are maps made primarily of rectangles, they show no elevation like a topographic map. They can also be called "line" maps, because they only show structures as a flat map. Planimetric maps can be very useful in city planning and drawling up counties. The above Planimetric map is of the Gowanus Canal in New York City. Showing roads, commerical, and industrial episodes with not further features of the land.
Continuously Variable Proportional Circle Map
http://www.esds.ac.uk/international/support/user_guides/gisoverview.asp
Continuously variable proportional circle map, is much like a proportional circle map but instead of the size of the circle representing a number, the circles are spread across a geographical area. Representing variables in "pies" across the map. These maps are very useful in showing age, or ethnicity across a population, each color on the pie representing the amount of that specific variable.
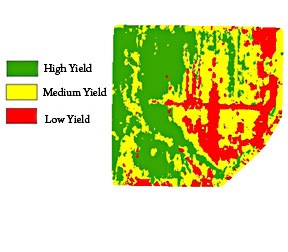
LIDAR
https://www.ars.usda.gov/is/pr/2010/100609.htm
LIDAR or Light Detection And Ranging, is a remote sensing tool that uses light and lasers to map different geographical areas. Measuring the distance from the laser with light helps them detect the different variables they are trying to find. LIDAR is used all throughout science, in geology, forestry, remote sensing and geomatics. The above LIDAR map is of the agricultural yeild possibilities of a piece of land.
DOQQ
http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/gis/doqq.html#bw
Digital Orthophoto Quarter Quads, or DOQQs are simply aerial photographs that are taken by the USGS. These are large scale photos that have a resolution of 1 meter. This particular DOQQ is an infrared photograph, they are taken in either infrared or black and white. This is an infrared DOQQ of Johnston County, Nebraska.
DEM
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_elevation_model
Digital elevation model is a high-tech way of showing elevated or three dimensional maps. DEM maps can show you the physical features of an area without being there, showing depressions in the land, or rises of mountains. The picture above is of the Tithonium Chasma on Mars, as you can see the different depressions and rises in the land of a place far away.
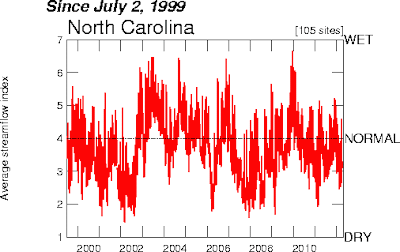
Index Value Plot
Index Value plots are used to statisically and graphically compare a variable. As you can see above the index value plot is showing the average stream flow of North Carolina. Index value plots are great for showing data across a longer time frame, like above it is showing the data from 10 years.
Classed Choropleth Map
http://go.owu.edu/~jbkrygie/krygier_html/geog_353/geog_353_lo/geog_353_lo07.html
Classed choropleth maps have all the characteristics of a choropleth map, and are considered "classed" because they have a key that tells you what the variable being shown is. Most choropleth maps are classed because of how difficult it would be to notice what an unclassed map is showing you. Both maps above are examples of classed maps because of how they show what the variable is by the key.
Unclassed Choropleth Map
Unclassed choropleth maps are simply a choropleth map that has no key which tells you what the different shades or coloring means. Choropleth maps are used to show many different types of data, because of how useful they can depict differences in data. So the map above can show you differences in states, but not what the variable is.
Bivaraite Choropleth map
http://proceedings.esri.com/library/userconf/proc99/proceed/papers/pap171/p171.htm
Bivarate choropleth maps are very complex graphing method of comparing two variables of a geographical relationship. Bivarate maps are commonly used in government statistical maps, and like other choropleth maps are very easy to interpret, but the process to create these maps are very complex. The map above is just showing the population densities of Ohio.
Standardized Choropleth map
http://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2007/oct/07_0091.htm
Standardized choropleth maps are used to show differences in variables, what makes them different is they keep the variable standard. This is a standardized choropleth map of poverty levels in the United States. Standardized choropleth maps are used to compare data, as you can see areas with high poverty are red, and dark red, while blue is low poverty.
Nominal Choropleth
http://my.ilstu.edu/~jrcarter/Geo204/Choro/
Choropleth maps are some of the most widely used and easiest maps for people to understand. Choropleth maps simply distinguish between places by different colors. To show the amount of male per 100 females in the 2000 US Census. Choropleth maps have different characteristcs from all maps and it is great for showing people differences in data.
Sunday, April 1, 2012
Lorenz Curve
A Lorenz Curve is a graphical representation of population wealth over percentage of population. Lorenz curves are primarily used in economics, and government. They are not limited to showing wealth vs. population it's what makes it easier to use. The Lorenz Curve above is a standard representation of what it should look like, with the 45 degree line being equality, and the curve being the actual data.
Population Profile
http://www.ifad.org/operations/regional/pf/aids_1.htm
Population profiles, or also known as population pyramids are very useful our ability today to compare population size and age. It stacks the data much like a stem and leaf plot, but on both sides so you can see male and female statistics. Most population pyramids don't have a second variable included like the one above. But in the one above it is a population pyramid of Botswana, and also compares the amount of population that has AIDS.
Climograph
http://met101.org/wiki/Climograph
Climographs are graphs used to show climate patterns, which shows the monthly averages of precipitation and temperature. It can give people an idea of a quick view of a climate of a specific place. Climographs are very useful because of how they show you two very important statistics of a certain place. The particular climograph above is comparing showing the temperature and precipitation levels for the Twin Cities.
Windrose
http://www.maine.gov/dep/air/meteorology/Windrosehome.html
Wind rose are graphs developed by meteorologists to display wind speed and direction from a central point. A wind rose got it's name simply from being a graph about wind, and how they distinguish the wind speed by color, making it look like a rose. The wind rose shows the direction that the wind has come from. The above wind rose is from a wind station in Maine.
Triangular Plot
A triangle plot, or ternary plot is used to compare three different variables to one constant. If the three variables don't equal the constant then a triangle plot is not possible. Mostly used in physical chemistry triangle plots are great for comparing the variables of three things, much like the USDA uses it in the above picture to test the three soil types. In the map or graph you can see how the three variables all sum to 100%, which makes it possible. It also simplifies the process of analyzing the data.
Histogram
http://www.vertex42.com/ExcelArticles/mc/Histogram.html
Histograms are graphical representations of the distribution of data. Histograms are comparable to bar graphs, in the sense that they represent the data in a very easy format for people to read. Histograms are most useful when plotting the density of data, for example the amount of people in the US. Most commonly used by the census. The histogram above is of the "Monte Carlo Simulation Results" which from the website I got it from, was just the example they used to show density distribution.
Box Plot
http://support.sas.com/documentation/cdl/en/statug/63033/HTML/default/viewer.htm#statug_boxplot_sect005.htm
Box plots are used to show the 5 number summary of data on a graph so people can more easily learn multiple things about the data. The bottom line shows the lowest number, the box is where 50% of the data is, top line is the highest number, and the middle line is the average. In a box plot you can learn all 5 of these things with one graph. The above graph shows the monthly power output, it is very useful in the situation of tracking the amount of data.
Stem and Leaf Plot
http://mainland.cctt.org/mathsummer/josephbond/stemandplots/stem-and-leaf_std.htm
Stem and Leaf Plots are a statistical way of organizing data to make it easier to compare. They're constructed by having the first number of the data on the left, "stem" and the seond number to the right, the "leaf." this lines the data so you can see where it is more easily spread. The plot above is showing the infant mortality rates in Western Africa, for example there would be 51, and none in the range of 60-70 because they have no "leaf."
Similarity Matrix
http://tomcat.esat.kuleuven.be/txtgate/tutorial.jsp
Similarity matrices are used to compare two sets of data. They are commonly used in DNA sequencing, helping comparing the different amino acids. Above is an example of a similarity matrix of proteins, as you can see the proteins that are not similar to the rest are slotted near the bottom.
Correlation Matrix
Correlation Matrices are used to statisticall compare two different variables, much like a scatter plot they test many different data entries at one time. The correlation matrix above shows the standard correlation between two variables. With no data, a common matrix would look something like the one above.
Star Plots
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radar_chart
Star plots are a complex system of mathematical equations used to show how the data measures up to the different ways you want to compare it. Each black line is a different characteristic you're testing for the data which is spread across the points, creating a star like the one above. Star plots are used to show many different variables, used in advanced departments like the one above created by NASA.
DLG
http://www.mapcruzin.com/free-geodata-shapefiles/usgs-geospatial-data-geodata-geographic-download.htm
DLG maps are straight-line or rectangular coordinate system maps that are created by mathematical equations and vectors. DLG maps are created by USGS maps, sold in three separate sizes. DLGs are used primarily in GIS (Geographic Information System.)
Isopleths
http://www.wbdg.org/resources/env_iaq.php
Isopleth maps are a type of contour map, isopleths must be taken over an area, not at a specific point. The above isopleth map shows the germination of mold and it's relation to % humidity and temperature. Isopleth maps can also be compared to choropleth map, because of how they both require a ratio of area and magnitude.
Isopach
http://seeps.geol.ucsb.edu/pages/isopach.html
Isopach maps use the elements of a contour map by using isolines to show variations in the data being shown. But the difference is it uses thickness within a unit, or "stratum." The map above shows the seepage of offshore coal oil.
Isohyets
http://www.scoop.co.nz/stories/AK0808/S00090.htm
Isohyets maps are newer maps that use lines to connect places that have similart rainfall patterns. Like isobars the closer they are together the more rainfall in that area. Isohyet maps use the different measurements from recording stations and then connects them to other recording stations by lines to give you a more complete picture of where the most rainfall is happening.
Isotachs
http://www.erh.noaa.gov/btv/events/28Oct2008/ua2.php
Isotach maps are much like a topographic map, isotach maps can show multiple different types of data. Mostly used to display details about wind, each detail in an istoach map shows something about wind. The black lines, (Isobars) show pressure changes, and the other bars show wind speed and direction. Also the color is used to show places that have the same wind speed.
Isobar
http://www.newmediastudio.org/DataDiscovery/Hurr_ED_Center/Hurr_Structure_Energetics/Closed_Isobars/Closed_Isobars.html
Isobars are used to create isoline maps, but are not limited to just being a part of them. They can also create different maps of there own, isboars simply distinguish between the variables being asked. In the map above the Isobar map is showing the pressure changes of North America. the closwer the bars get together the higher the pressure is, and as they become more spread out the pressure lowers. With the result of a low pressure system in the middle.
Doppler Radar
Doppler Radar is used mostly in weather, because of how easy it can be used to display to the public. It is a very advanced system of mathematical equations that help measure the reflectivity of clouds. The radar above shows a storm advancing into Oakland, Wisconsin. You can see the differences in severity by the color change, red being the worst, and blue being calm.
Infrared Aerial Photo
http://www.krisweb.com/krissheepscot/krisdb/html/krisweb/watershed/urban.htm
Infared photography is very useful in todays modern world, espcially for the use of military needs. It distinguishes between places of high and low heat. Infared in maps can be used to show differences in population, agricultural uses, or to show places that have been highly effected by industrialization. In the above picture it is showing the effects of urbanization on the water flow in the Gulf of Maine. Areas in red are places that were highly effected by urbanization.
Isoline Map
An isoline map is used many different ways, what defines an isoline map is the use of lines to distinguish between the amount of the variable being shown. Isolines are very user friendly and in most cases like the one above they fill the different isolines in with color to make it even easier to interpret. The above map is of the state Washington and the amount of rainfall in 1996. You can see how the lines and colors distinguish between the amount of rainfall.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)